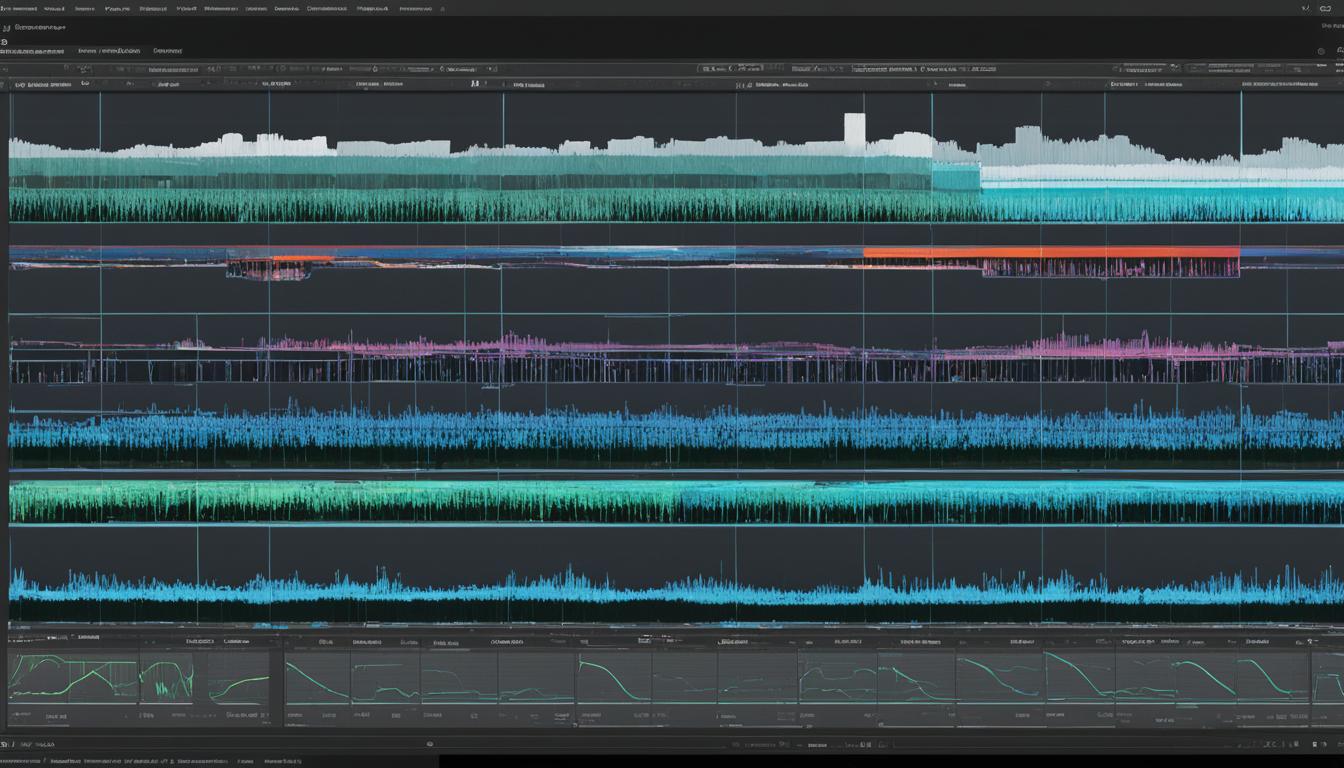
The world of videography is vast and variegated, each technique holding the potential to tell a story in a myriad of shades. Among these, raw video stands as the film’s unpolished jewel—coveted for its purity and potential. A raw video definition encapsulates the essence of imagery at its most authentic, drawing a parallel to the revered film negative from yesteryear’s storied cameras. It is this unmanipulated sensor data—a storeroom of pixels—that videographers in South Africa and beyond weave into visual masterpieces.
In this comprehensive guide to raw video format, we delve into the heart of what is a raw video and explore its pivotal role within South African videography. We’ll dissect the layers of freedom that raw video avails to the discerning editor and elucidate why this format is cherished in the professional arena for its unparalleled fidelity and adaptability.
Key Takeaways
- Raw video embodies the untainted sensor data from a video capture device, preserving the full spectrum of pixel information.
- Essential for intricate post-production, raw video caters to substantial adjustments in exposure and color grading without quality degradation.
- While offering editing latitude, raw files are substantially larger, influencing storage considerations and workflow strategies.
- Formats like ProRes RAW and BM RAW cater to proprietary workflows but present compatibility challenges in a diverse editing landscape.
- The higher investment in storage infrastructure due to raw video’s sizable nature is offset by its post-production merits.
- Understanding raw video is crucial for video professionals aiming to elevate their storytelling in the competitive creative industries.
What is a Raw Video?
At the heart of high-end videography lies the concept of raw video footage—the purest form of visual data one can capture through a camera. In examining the raw video meaning, we delve into the nuances of sensor data as it translates into unprocessed video output. This medley of red, green, and blue at each sensor point can be likened to an artist’s palette, waiting for the post-production brush strokes that will define the visual story to be told.
The Fundamentals of Raw Video Capture
Raw video production is centered around capturing all the sensor data from the camera without any in-camera processing. This prevents the loss of crucial details and maintains the integrity of each pixel—allowing for extensive post-production control. Whether it’s correcting shooting errors or fine-tuning the visual output, the raw video file becomes a versatile tool in any videographer’s arsenal, optimizing the potential for a high-quality video result.
Raw Video vs. Standard Video Formats
It’s important to differentiate between raw video vs edited video. Edited or standard video formats typically undergo significant camera processing that can introduce unwanted image artifacts and reduce overall quality. These formats prioritize smaller file sizes over image integrity. On the contrary, raw video footage remains untainted by such alterations, preserving the full dynamic range and enabling superior image control in the later stages of video editing.
Advantages of Shooting in Raw Format
Opting for raw video translates into unmatched post-production latitude. From manipulating exposure and white balance to intricate tweaks in color grading and sharpness, raw video stands unrivaled. Such a range of adjustability is of particular importance in scenarios with challenging lighting or when a specific visual ambiance is essential. Nonetheless, those considering the raw pathway must also brace for the impacts of larger file sizes and the accompanying storage and cost considerations inherent to raw video production.
| Feature | Raw Video | Standard Video |
|---|---|---|
| Image Quality | Highest possible, no loss of details | Lower, due to compression and processing |
| Post-Production Flexibility | Extensive control and manipulation | Limited by loss of data and compression |
| File Size | Large, requiring more storage | Smaller, more manageable for casual use |
| Suitable Applications | Professional production with high-quality output | General use, casual videography, quick sharing |
Raw Video File Characteristics
The intricacies of raw video editing are closely tied to the substantial raw file size of the footage typically used in the process. As an uncompressed or lightly compressed format, raw video encompasses the entirety of the visual data captured by the camera’s sensor. This results in a vast amount of information that requires considerable storage space impact management.
Uncompressed raw files, stark in their pure size and quality, are a testament to the saying “size matters” in videography. We’re dealing with files that are leagues above the standard in terms of data density. Consider this: a single second of uncompressed raw HD video can tip the scales at a colossal 150MB, assuming a standard frame rate of 30 frames per second—with each frame encapsulating approximately 5MB.
| Resolution | Frames per Second | File Size per Frame | Total File Size per Second |
|---|---|---|---|
| HD 1080p | 30 | 5MB | 150MB |
| 4K | 30 | 20MB | 600MB |
| 8K | 30 | 80MB | 2.4GB |
For professionals and passionate enthusiasts who are willing to navigate the nuances of raw video editing, the expansive data becomes a canvas of creative opportunities. However, the magnitude of uncompressed raw files can be daunting, especially when we consider the additional considerations of backups and archiving.
It’s crucial to note that the storage space impact doesn’t merely stop at needing more gigabytes or terabytes on hard drives; it extends into the realms of investment in faster, more durable, and technologically advanced storage solutions. These can range from high-speed SSDs to expansive RAID systems designed to not only store but also protect the invaluable raw footage.
The decision to use uncompressed raw footage revolves around a trade-off, a delicate balance between quality and practicality. Videographers must measure their need for the highest possible fidelity against the realities of managing and storing overwhelmingly large video files. Without a doubt, uncompressed raw footage stands as the zenith of image quality and post-production flexibility, but it asks for a commitment to infrastructure that some may find too steep a price to pay.
“The future of video editing hinges on the ability to store and manipulate ever-growing raw file sizes without breaking stride. This is the horizon we’re heading towards—an era where storage space impact is a challenge overcome by innovation.” – Industry Expert on Raw Video
Editing and Post-Production of Raw Footage
Embarking on the journey of editing raw video footage can be both rewarding and challenging for a professional videographer. The process tests the technical resources, ingenuity, and patience crucial for transitioning the visual narratives from their nascent stages to compelling pieces of art.
Challenges of Editing Raw Video Files
Among the most prominent post-production difficulties is the sheer size of raw files. These gargantuan packets of data strain even the most high-capacity storage systems and require a formidable setup with state-of-the-art editing software. Faced with the potential for lag and system crashes, editors must assemble a machine with an optimal GPU, CPU, and an abundance of RAM to ensure the smooth sailing of raw video editing.

Color correction and audio synchronization compound the complexity. They introduce additional layers to the workflow, demanding a keen attention to detail and profound technical knowledge from the professional who navigates these choppy post-production waters.
Tools and Software for Raw Video Editing
For professional video production, a suite of sophisticated editing tools comes to the rescue to efficiently manage and manipulate raw footage. Names like ProResRAW, Blackmagic RAW, and REDCODE RAW dominate the toolkit, each offering distinct features that cater to various editing needs and preferences. Their integration with advanced GPUs is non-negotiable, as this synergy is essential for ensuring a responsive and uninterrupted editing experience.
Raw Video Workflows for Professionals
The raw video production workflow demands a strategic approach right from the initial stages of capturing footage. Essential steps in the process involve the deployment of high-capacity storage media, such as professional-grade flash cards, and the use of efficient data transfer systems to secure the integrity of the raw files.
Arranging the settings on high-end cameras for raw data capture and considering alternative shooting methods, like shooting in LOG format, are decisions made with foresight. These decisions significantly affect the storage needs and flexibility in post-production. A balance between quality and storage economy is struck, ensuring that the artistic vision is not compromised by technical limitations.
In sum, the craft of transforming raw video footage into a polished final product is a detailed dance of technology and creativity. It requires a measured hand capable of wielding the powerful tools that render the raw canvas into a masterpiece worth the audience’s attention.
Conclusion
The profound impact of raw video on the landscape of video content creation cannot be overstated. This format has irrefutably changed the game for filmmakers, allowing them to manipulate footage in post-production with a finesse that was previously unachievable. The significance of raw video is rooted in its ability to preserve the pristine quality of the captured images, bestowing editors the superlative power to refine and alter visuals to align with their creative vision.
In the context of the South African film industry, this means that content creators are now equipped with the tools to pursue excellence in visual storytelling. The endless possibilities for color grading, exposure adjustment, and detail manipulation are essential for productions endeavoring to stand out amidst the competitive arena of international cinema.
Understanding the dynamics of raw video is more than a technical requirement; it is a strategic advantage in the modern era of filmmaking. As the industry in South Africa continues to flourish, the assimilation of raw video workflows will be pivotal in harnessing the full potential of digital video technology, propelling South African creators to new heights of innovation and expression.
FAQ
What is a raw video?
A raw video is the unaltered, unprocessed sensor data captured directly from a camera, which provides maximum flexibility for post-production editing. It preserves the highest quality of footage by recording all the information that the sensor reads, similar to a digital negative in photography.
How does raw video differ from standard video formats?
Unlike standard video formats, which are processed and compressed in-camera, raw video maintains all sensor data without any alterations. This results in higher quality footage with no image artifacts that can be extensively manipulated in post-production. Standard formats often discard surplus information to reduce file size, which can limit editing capabilities and degrade image quality.
What are the advantages of shooting in raw format?
Shooting in raw format offers a range of advantages, including increased control over editing aspects like exposure, white balance, color grading, and detail enhancement. It provides greater latitude for correcting mistakes made during filming and for aligning the final image with the filmmaker’s vision without degrading the quality.
What does raw video footage mean for file size?
Raw video footage generally implies much larger file sizes due to the lack of in-camera compression and the preservation of all image data. This can mean increased storage requirements and potentially higher production costs to accommodate the additional data.
What challenges arise in editing raw video files?
Editing raw video files can be challenging due to their large sizes, which require powerful computing hardware with advanced GPUs and substantial RAM and storage capacity. Videographers must also address the complexity of color correction and audio synchronization during post-production.
Which tools and software are preferred for editing raw video?
Professional video editors use advanced software tailored for raw video editing, such as Apple’s ProRes RAW, Blackmagic RAW, and REDCODE RAW, which are designed for efficient processing and ease of editing. These software applications leverage powerful computing resources for handling demanding raw video workflows.
How do professionals manage raw video production workflows?
Professionals manage raw video workflows by leveraging high-capacity storage media, swift data transfer methods, and meticulous technical prep, such as ensuring the camera’s settings are configured for raw capture. They may also use intermediate formats like LOG to retain detail while conserving storage space compared to full raw files.
Why is raw video significant in content creation?
Raw video is significant in content creation because it offers unrivaled flexibility and maintains the highest image quality throughout the production process. This allows creators to finely tune their output in post-production, ensuring that the final product matches their artistic intent and meets professional standards, which is particularly beneficial in markets such as South Africa’s growing film industry.